Eruption hematoma (Eruption cyst)
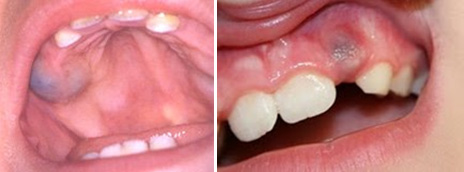
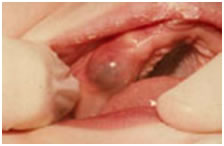
A bluish purple, elevated area of tissue, commonly called an eruption hamatoma, occasionally develops a few weeks before the eruption of primary and permanent tooth. The blood-filled cyst is most frequently seen in the primary second molar or the first permenent molar regions. This is due to the gums becoming thin in front of the erupting tooth and some minor trauma to the soft tissue during function causing a hematoma in that area. Usually witin a few days the toothbreaks through the tissue, and the hematoma subsides. Because the condition is is almost always disappears spontaneously, treatment of an eruption hematoma is rarely necessary. However, surgically uncovering the crown may occasionaly be justified.
Sources
McDonald RE, Avery DR, Dean JA. Eruption of the teeth: Local, systemic, and congenital factors that influence the process. In: Dean JA, Avery DR, McDonald RE. Dentistry for the child and adolescent. St. Louis, Mosby Elsevier, 9th ed., 2011, p: 150-176.





