Pediatric and Orthodontic Dental Services
We offer dental services for infants, children, and adolescents along with orthodontic services for both children and adolescents.
Preventative
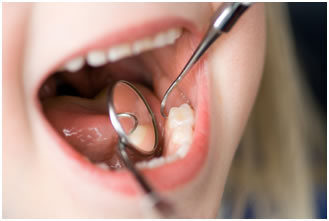
Initial exam: Includes general review of the child’s or adolescent’s medical and dental history, general examination of face, head and neck. Your child will receive an examination of teeth, bite, gums and overall dental development.This includes a thorough examination of the soft tissue in the mouth.This is done in a minimally invasive fashion so that your child feels comfortable and safe. We also determinean individualized risk assessmentfor dental diseases and conditionsof an infant, children or adolescent patients.Additionally, parents are given an information of preventative home care (brushing/flossing/fluorides), a caries risk assessment, information on finger, thumb, and pacifier habits, advice on preventing injuries to the mouth and teeth of children, diet counseling, and information on growth and development.
We will also provide an oral hygiene instructions, necessary teeth cleaning, fluoride treatment, and obtain the appropriate radiographs.Using the information from the examination and x-rays, we assemble an appropriate treatment plan to ensure optimal dental health.Treatment as indicated by the diagnosis will be provided at subsequent appointments.
We prefer not to perform any restorative procedures in children at first visit unless it is a emergency. By doing that we are able to establish the first connection with them in such a way as to build on a relationship of trust.
Oral hygiene instructions:

Oral hygiene instruction’s primary purpose is to educate and train the patient in order to develop excellent oral hygiene skills for controlling the dental plaqueeffectively that causestooth decay and gum disease. Oral hygiene is performed at initial visit and every recall visit.
The plaque on teeth revealing by a disclosing tablet or gel. The tablet or gel contains a dye that binds to plaque when it is applied. After rinsing, the teeth are examined to identify areas of high plaque build-up. The use of disclosing materials can help improve brushing and flossing of teeth by highlighting missed areas.This plaque disclosing materials will not only tell you where there is plaque on your teeth, but also it will provide some information on how long that plaque has been there and if it is likely to damage your teeth.
After the oral hygiene instruction, a prophylaxis is performed as needed. During this procedure, deposits of plaque, calculus and stains are removed from the surfaces of the teeth.
 |
 |
| A | B |
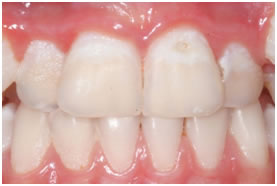
A.Heavy dental plaque accumulation on teeth.
B.After rinsing the mouth, plaque accumulation on teeth is more visible for the patient.
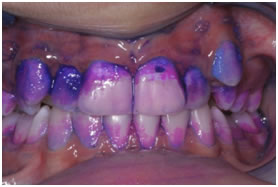
Pink- Indicates new or young plaque in place within 24hrs.
Blue/Purple - Indicates old plaque that has matured and been in place for more than 48 hrs.
Light Blue - Indicates plaque that is actively producing plaque acids causing cavity (Extra high risk plaque).
Recall visits:

A happy caries-free and healthy child at recall visit.
The patient will return for an oral health review,during which the histories and examination will be updated and any changes in risk factors noted at recall exam. This is for the existing patients whom regularly seen at the dental office. It is an opportunity to do an oral examination and interpretation of radiographs if they have been updated to ensure that no problems have arisen since the last examination. It will be also checkedthe effectiveness of the restorative and preventive treatment provided previously, and will perform more treatments as necessary. Oral hygiene intructions are demonstrated at every recall exams. Recall exam is also important for the child patients to monitor the loss of primary teeth, and the progression of dental development.The amount of time between recalls is individualized to meet each patients needs. For some, 6 months is appropriate, while for others, we may want to see you more frequently at 1, 3 or 4 month intervals to address a specific concern.
Topical fluoride applications:
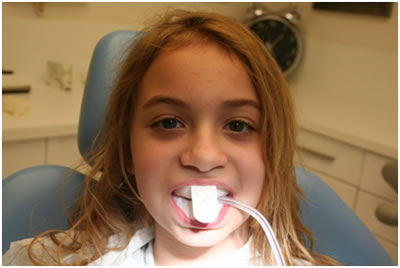
Topical fluoride application in the gel form.
Topical fluoride is a caries preventive agent applied to tooth enamel. It comes in a number of different forms. A dentist places gels or foams in trays that are held against the teeth for up to four minutes. Topical fluoride is used to prevent and treat dental caries. Acidulated phosphate fluoride, or APF, preparations, which have been accepted by the American Dental Association since 1968, contain 1.23 percent fluoride ion (12,300ppm).Fluoride varnish is brushed or "painted" on the enamel. Varnish is especially useful for young patients and those with special needs who may not tolerate fluoride trays. Children who benefit the most from fluoride are those at highest risk for decay. Risk factors include a history of previous cavities, a diet high in sugar or carbohydrates, orthodontic appliances, and certain medical conditions such as dry mouth.
Teeth cleaning: The most seen staining problem in primary or the mixed dentition is the black stain.The black stain, which is most often seen near the gum line on on both the front and back of the teeth of children, is the result of the action of chromogenic bacteria.An investigation has been carried out into the nature of the black pigment in black extrinsic tooth stain. The results suggest that theblack material is a ferric salt, probably ferric sulfide, formed by the reaction between hydrogen sulfide produced by bacterial action and iron in the saliva or gingival exudate.The intensity of stains may be worsened if there are enamel defects. Many children who have black stain are either caries-free or with a low caries frequency. Iron-containing oral solutions used for treatment of iron deficiency anemia or multivitamin syrups also cause black stains.
Black stains can be removed by polishing with a rubber cup and fluor pumice using pressured water. Because stains are most often seen in mouth in which there is poor oral hygiene, improving the oral hygiene minimizes the recurrence of the stain.
Sometimes children and adolescents have tartar problem. A cleaning done at the dental office is important in keeping your child’s gums and teeth healthy and strong. An office cleaning uses a prophylaxis paste. This procedure removes stains on teeth caused by food or certain bacteria and tartar.
Dental radiography (X-rays):Dental radiographs are taken only when there is an expectation that the diagnostic yield will affect patient care. The “as low as reasonably achievable” (ALARA) principle is followed to minimize exposure to radiation for our patients.
We use Schick CDR digital radyography systems at our clinic.

Dental sealants:
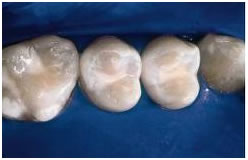
Sealants play an important role in the prevention of tooth decay by protecting the chewing surfaces of teeth. Sealants keep out plaque and food, and reduce the risk of tooth decay by filling in pits and fissures on the chewing surface of molars. Sealants are used to fill in narrow grooves in a tooth that cannot be adequately cleaned by brushing. At your child’s regular dental exam, their sealants are evaluated and maintained or replaced as needed. Since the sealant is only on the biting surface of the tooth, areas on the side and between teeth are still at risk for decay. Good oral hygiene and nutrition continue to be very important in preventing decay. A total prevention program includes regular visits to the dentist, the use of fluoride, daily brushing and flossing, and limiting the number of sugar-rich foods that are eaten.
 Sport Mouth Guard: A mouth guard offers protection during any activity that could result in a blow to the face or mouth. A properly fitted mouth guard can help prevent broken teeth and injuries to the lips, tongue, face or jaw. If your child is actively involved in sport activities please inform us at the initial exam.
Sport Mouth Guard: A mouth guard offers protection during any activity that could result in a blow to the face or mouth. A properly fitted mouth guard can help prevent broken teeth and injuries to the lips, tongue, face or jaw. If your child is actively involved in sport activities please inform us at the initial exam.
Appliances for Oral Habits :The sucking reflex is natural for infants, and often begins in the womb. As your child grows, they may be sucking their thumbs for a purpose. It can make them feel secure, happy or they could be soothing themselves to sleep.
Once the permanent teeth begin to erupt, thumb or finger sucking can become aproblem. It could interfere with the proper growth of of the jaws, and teeth alignment. Changes to the roof of the mouth could also occur, depending on the intensity of your child’s thumbsucking.Somechildren have other oral habits such asthe two most common are a thumb or finger habit and a tongue-thrusting habit.Habit appliances are devices designed to prevent oralhabits.If you think your child has either of these habits, call us today for an appointment.
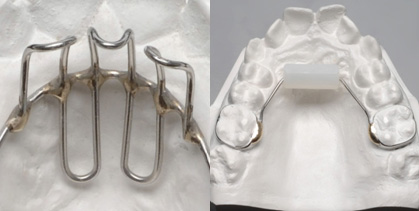
Different habit appliances
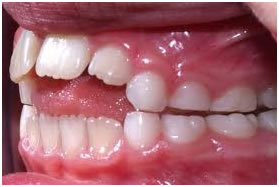
Open bite - caused by thumb sucking and tongue thrust
Orthodontic Treatment and Appliances:

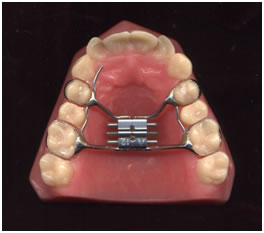

Pediatric Dentists have a chance to evaluate a child’s bite at an early age and monitor growth and development. Bite problems such as cross bite, open bite, over bite should be treated early to allow for proper growth of face and jaws. Teeth in incorrect positions undergo abnormal wear and tear compromising appearance and function.
We provide both interceptive and comprehensive orthodontic treatment for pediatric, and adolescent patients.
Space Maintainers:When a primary tooth is lost early through trauma or tooth decay, adjacent teeth could shift and begin to fill the empty space. When permanent teeth emerge, there's not enough room for them and this results in crooked or crowded teeth and difficulties with chewing or speaking. A space maintainer is used to hold the spot left by the lost tooth until the permanent tooth emerges.
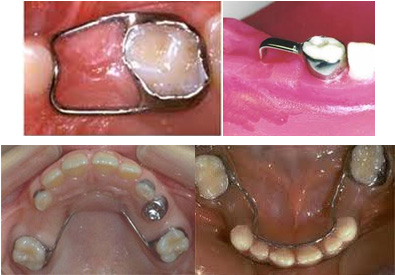
Different types of space maintainers
Restorative Procedures:
Composite/resin fillings :White fillings or composite/resin fillings: They are mercury-free non-metallic fillings. This is the only material used for filling teeth in our office. We do not use any material that contains mercury.

Pulp Treatment (Pulpotomy/Pulpectomy): Inside each tooth is the pulp which provides nutrients and nerves to the tooth, which runs down through the root. When the pulp is diseased or injured by severe decay, the pulp tissue dies leading to infection and a dental abscess. In place of removing the tooth, the pulp is treated which allows the tooth to remain in the mouth until the end of its natural life. The procedure involves removal of dead tissue and placement of medicated materials in the root canal. Following this, a composite resin filling or a stainless steel crown is placed over the tooth.
 |
 |
Pulpotomy |
Pulpectomy |
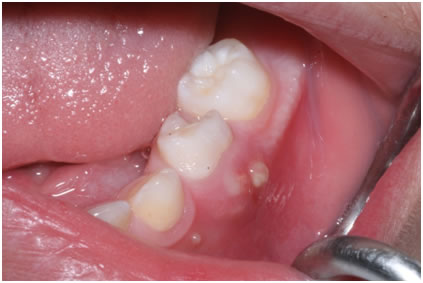
Dental fistula
Stainless Steel Crowns/Pediatric Strip Crowns: A crown is necessary when extensive decay removal or after pulp theraphy. A crown can make the tooth stronger and improve its appearance by restoring its shape and size. Pediatric strip crowns are transparent plastic crown forms used for restoring primary anterior and posterior teeth. For front teeth a stainless steel crown with white facing or strip crown is used and for back teeth an all stainless steel crown or strip crown is used.
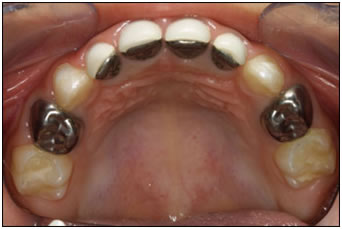
Stainless steel crowns


Pediatric strip crowns
Extractions: Teeth are extracted or removed when they are unsaveable by any treatment. This may be due to decay, infection or trauma. With careful use oftopical anesthetic and local anesthetic, extractions are performed on children with minimal discomfort.
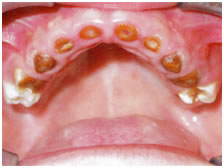
Teeth loss due to early childhood caries
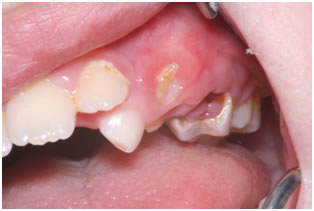
Primary molars are lost due to dental neglect
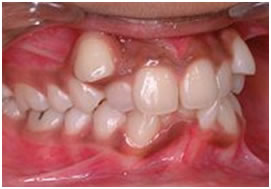
Teeth are also extracted for orthodontic reasons when there is inadequate space in the jaws to accommodate all teeth.
Ectopic eruption: Occasionally, a permanent tooth begins to erupt before your child's primary tooth falls out. It erupted lingually of the primary tooth. This is called an ectopic eruption. Lingual eruption of mandibular incisors is a common clinical problem in the early mixed dentition period. In these cases it is to follow up the resorption of primary tooth’s root resorption radiographically and the eruption of first permanent molars whether or not to extract of the primary tooth.
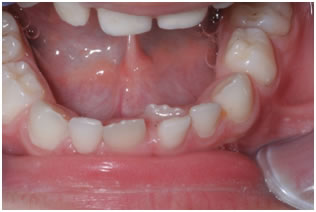
Ectopic eruption
Comprehensive Dental Treatment under General Anesthesia:A child may be recommended for dental treatment under general anesthesia in a hospital setting for the following reasons: young age of the child, special medical conditions, extensive dental needs, or challenging behavior. General anesthesia is a controlled state of unconsciousness that eliminates awareness, movement and discomfort during dental treatment. General anesthesia renders your child completely asleep. When this is the case we perform their dental treatment safely under general anesthesia at a hospital setting in Acibadem Kozyatagi Hospital.
Sources
http://www1.umn.edu/dental/courses/dent_5501/till_handout02.pdf
http://proofs.pbhs.com/pediatric/schroeder/pediatric-dentistry-wenatchee-wa/appliances.html
http://www.westsideladentist.com/2011/04/what-are-space-maintainers-and-how-are.htl
http://uniortholab.com/products.htm
http://www.nature.com/bdj/journal/v206/n3/full/sj.bdj.2009.56.html
http://www.kokkinosmileclinic.com/crowns.php
http://www.provisionalmatrix.com/shop/pediatric-strip-crowns.asp
http://www.irinadental.com/index.php?page=problem&pro=crowding&page_name=Crowding





